‘Geographic Information System’ and its application in Earth Sciences
Geographic Information Science (GIS) provides powerful Innovations in transportation, tracking the locations and structural composition. The use of GIS has seen magnificent growth in the last ten years. It has become a core part of the modern environmental-related study, Geology, climatology, geography, archaeology, oceanography, and other relevant science.
GIS is something that will make many problems easier and faster and allow them to do more things in the same space of time with the click of a button. The professionals with the uses of Digital Map gather, analyze, manipulate and visualize geographic data about our world and even other planets.
Maps are not the exclusive preserve of the cartographer, now urban and rural developers, medical resource planners, environment agencies (to manage and measure floodplains and the spread of protected species) and archaeologists also benefited from the digital map. The geographic Information system also plays a vital role in scientific research. With broad applications of spatial data and visualizations in earth science, we can explore growing our understanding of earth science and new happening around it.
What is GIS?
GIS or Geographic Information Systems is a tool that captures geographic data for the purpose of multiple information, viewing, and analysis in whichever context and parameters the user desires or needs. GIS can be used to analyze spatial data or geographic information for any given and desired purpose.
GIS in Geology
Geologists investigate the planet’s structure, composition, earth resources, and environmental-related issues. However, it’s not possible for scientists to visit a location for field observation. The application of Geographical information systems in geology means scientists can use electromagnetic radiation to collect detailed information from all over the world.
Interpreting and visualizing the data received from remote sensors are among the primary uses of GIS for geologists. GIS experts map out the earth’s surface, its features and offer complete data to natural resource management.
For example, The Geological Survey of India provides researchers and organizations with a high quality of geological and GIS data, such as topographic details for the entire country and interactive maps of the coastline. With detailed spatial information, it is also possible to model subsurface water resources and assess the stability of terrain for oil and gas exploration.
Applications of GIS
Disaster Management
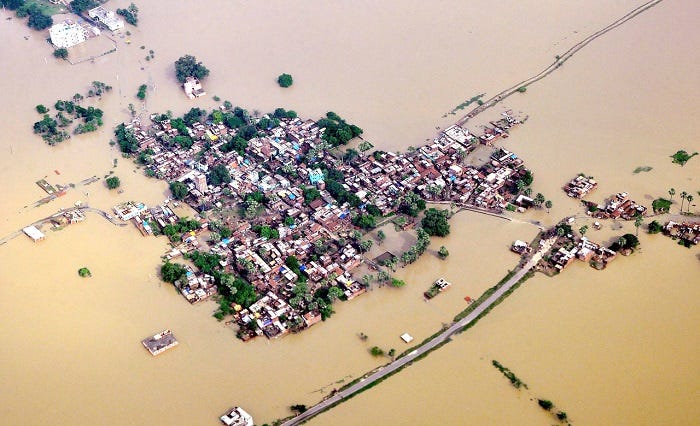
As said GIS is being used to manage environmental Hazards and in disaster relief. Environmental experts have plotted the instrument in the affected region and with the newly available technology, GIS is the first responders on the ground about Tsunami (Hurricane and Katrina), Earthquake and other Natural Hazards.
Particularly when a tsunami already hits the ground and everything is destroyed, the GIS is the only tool to tell which streets were and were not accessible and the extent of the flooding. GIS can give an accurate set of data about the affected area.

Spatial data is particularly valuable in the mining industry, where mineral exploration using remote sensing and GIS leads to effective prospecting. Organizations identify the probable locations of deposits by mapping surface features and performing spectral analysis in search of accuracy in chemical interaction.
Many countries having the departments of Mining and Minerals Division. These Department uses GIS to process permit applications and keep current data about mining activity. With this information, regulators have the visibility to enforce compliance, maintaining safety standards, and mitigating impacts on the environment.
Archaeology
Archaeological investigation often involves systematic field surveys to invent cultural features and artifacts visible on the ground surface of a particular site or region. These inventories are then used for overall spatial study based on artifact types found on the ground. After finding relevant and sufficient initial information make decisions about which areas within a site will receive priority when conducting traditional ground excavations.
यह भी पढ़ें- Machu Picchu’ the World Heritage site and secrets behind it. Take a Geotourism around this Marvel
There are many applications of GIS in the field of Archeologist research. Sometimes the historic site buried below the ground. To identify these prehistoric sites and areas that may have the potential for future on-the-ground research, GIS is more beneficial than any other tool.
Oceanography
The vastness and complexity of Earth’s oceans required specialized software which may focus on marine ecosystems to plate tectonics. The application of GIS in oceanography assisting researchers by giving them tremendous opportunities to prospect the underwater world.
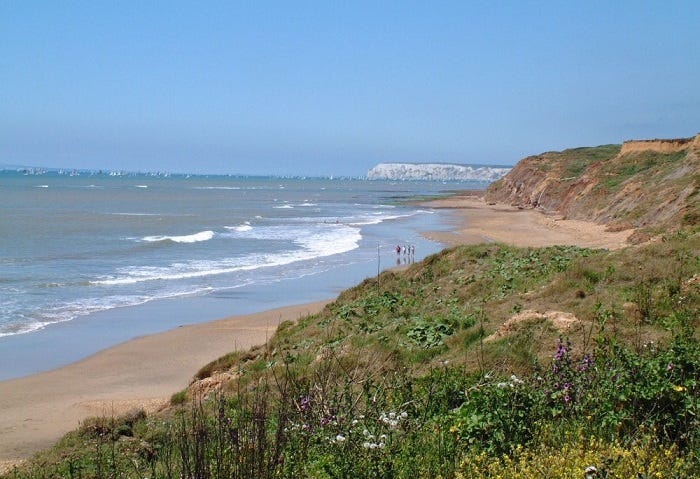

For example, the ArcGIS Ocean Basemap offers data about the seafloor and coastal regions, including depth values and the names of features.
Transport
Because of the massive amount of planning and infrastructural development, it is beyond the human being to plan and execute such amount of data at a time. But with the use of GIS, these massive amounts of data can avail and collected at a time with the use of a dedicated GIS site.
Many public works including High-Speed rail connectivity, highway up-gradation, and another such type of projects can be monitored from a room by the use of GIS Application software.
Civic Planning
GIS has been an excellent tool for rural and urban planning for the last few decades. As the world continues to move towards urbanization, the need for effective urban planning continues to grow. We need highly specialized GIS equipment and advanced software to achieve our objectives.
GIS finds its place in urban planning as an analytical and modeling tool. It is also useful in monitoring an area or conducting a feasibility study of a location for a specific purpose, e.g. for the construction of a bridge or dam. Now feasibility study of even smaller structures like schools and hospitals is also an essential part of the GIS study.



